ITA/ENG
DIRECTOR AND SCIENTIFIC RESPONSIBLE
Maurizio Carta
RESEARCH UNIT
Alessandra Badami
Daniele Ronsivalle
Valeria Scavone
TECHNICAL-SCIENTIFIC STAFF
Annalisa Contato
Carmelo Galati
Raffaella Riva Sanseverino
Claudio Schifani
Carla Tumminello
COLLABORATIONS
Barbara Lino
Jessica E. Oliva
TRAINEES
Marina Bonomolo
Gabriella Di Filippo
Davide Emmolo
|

viale delle Scienze, ed. 14, Corpo C, stanza 109
|
 |
 |
|
SMARTPLANNING.master
The education activities of the SMART PLANNING LAB are offered by the Master Universitario di II livello in "Pianificazione integrata per lo sviluppo sostenibile del territorio",
COORDINATOR
Prof. Maurizio Carta
SCIENTIFIC BOARD
Maurizio Carta, Umberto La Commare, Vincenzo Provenzano, Alessandra Badami, Ignazio Vinci, Daniele Ronsivalle
FACULTY
Alessandra Badami, Maurizio Carta, Alessandro Ficile, Andrea Gumina, Umberto La Commare, Cleo Li Calzi, Barbara Lino, Marilena Orlando, Andrea Pillon, Gianfranco Rizzo, Daniele Ronsivalle, Claudio Schifani
ACADEMIC YER 2013-14
The education activities are placed at Polo Universitario di Ricerca di Bivona e Santo Stefano di Quisquina per l’Energia, l’Ambiente e le Risorse del Territorio (sede di Bivona - AG) and at the Department of Architecture (Palermo, viale delle Scienze).
The Master is funded by the Regione Siciliana, University of Palermo, the Provincia Regionale di Agrigento, the Municipality of Bivona and the Municipality of Santo Stefano Quisquina for the implementation of the POLO UNIVERSITARIO DI RICERCA DI BIVONA E SANTO STEFANO DI QUISQUINA PER L’ENERGIA, L’AMBIENTE E LE RISORSE DEL TERRITORIO
|
| |
|
|
#SMART PLANNING LAB: THE POWER ENGINE OF SMART AND GREEN CITY
“A Smart City needs the integration of technological and social components with the urban development model, within a vision that produces cities more intelligent, more sustainable and more inclusive, not just inputting technology, but generating innovation. To achieve this integration, the Smart City must adopt a model of planning/management of urban life cycles that is able to consistently integrate the ICT components with those of governance and the decisions about the location of main urban functions. In accordance with the system integrator’s vision, the Smart Planning Lab is a fundamental part of the i-NEXT Project”.
#MISSION
The Smart Planning Lab is an operational tool that integrates applied research, communication and education in the i-NEXT Project (Innovation for greeN Energy and eXchange in Transportation), funded by the Italian Operative Program "Research and Competitiveness". It carries out three main functions:
1) at an early stage as a producer of context and scenario analysis, and as a producer of solutions aimed at a new and more efficient regulation of life cycles and the localization of actractive urban functions (cultural, economic and social).
2) In the intermediate stage as "intelligent hub" that allows a constant connection with the needs of urban planning and management, using sectorial analysis or operational proposals and developing guidelines for urban governance and integrated planning for the sustainable development.
3)being permanent as a tool of communication and dissemination of methods and outcomes of the Project, contributing to the strengthening of the necessary "Smart Citizenship and Social Innovation". It will report a responsibility to produce information documents, including digital and on the cloud, and non-technical intermediate reports that allow to spread the Project both locally and in respect of the Italian Ministries interested, but also in respect of other cities engaged in the trials of urban smartness also in order to constitute a "Smart Cities Network".
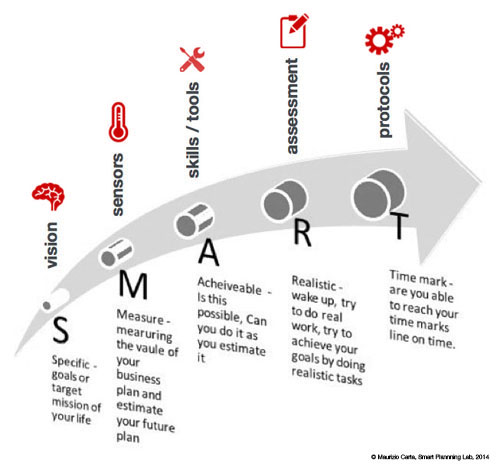
The Smart Planning Lab is an activator of education and training functions and retraining as fallout of the Project and its sustainability after the phase of Ministerial funding:
• training and technical upgrading for public administrations in the processes of "creative, smart and green" urban regeneration;
• technical assistance services to both public administrations that the private sector for the implementation of the addresses identified and action plans drawn up with reference to the actions provided for in the Europe 2020 Strategy and Horizon 2020;
• development of ICT services dedicated to the themes of the Project to be introduced in the network of digital citizenship for increasing the participation and sharing in "green and smart oriented" development programs;
• activities of information and dissemination for the growth of smart citizenship and social innovation.
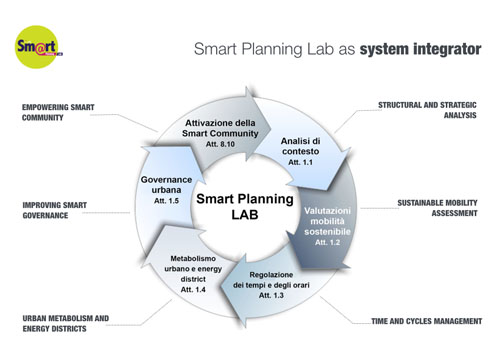
#HORIZON: CLOUD GOVERNANCE
We are increasingly immersed in the society of knowledge, of creativity and innovation, today universally regarded as the key to competitiveness, true anti-cyclical factors with respect to the crisis that has overrun the capitalist development protocols Which requires processes of knowledge creation, spread and replacement. It requires a constant, powerful and pervasive flow of knowledge, exchange of information, and instant evaluation about the effects of government actions. Innovation has no boundaries, it affects each and every an aspect of institutions and enterprises and operates as a "mutagen" of society, requiring a paradigm shift to whom bears the responsibility of governing under the aegis of a renewed leadership.
From global to local economies and back: this is the challenge all leadership around the world are facing today, both at the national, local or business level. The infertile opposition between global and local is no longer an option, as they are deeply connected by the Network Society, and so is the ambiguous definition of "glocalization" with its recent load of rhetoric, lacking operational substance if compared to the first pioneering experiences. The new path ahead of the world socio-economies today is to draw on the long network flows, transforming them through spatial patterns into energy for local systems. These flows, once diversified into veins of identity, generate value in the local realm to be re-entered in the large global corridors that will thus be revitalised, nurtured, characterized and differentiated.
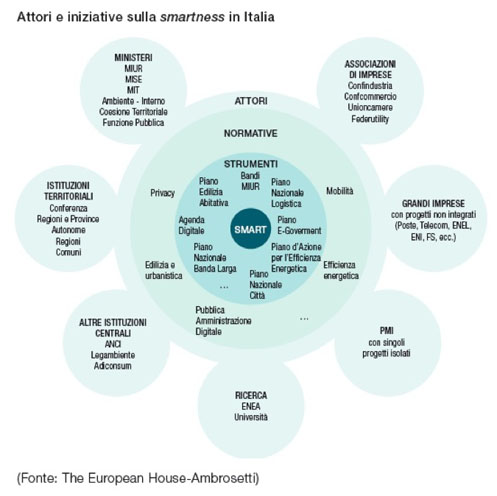
#CHALLENGE: OPEN SOURCE URBANISM
The mutations not only do changes affect the economic and relational realm, but they are being, with growing pervasiveness, transferred to the physical realm, as regards physiognomy and physiology of the cities, intelligent. However, a smarter city is not the one whose traditional organization boasts the most intelligent and efficient technology, but the city that profoundly alters the development dynamics and revisits its housing and mobility patterns rethinking its metabolism through efficient urban cycles. Increasing the infrastructural smartness is not sufficient, as cities ought to endeavour to increase the rate of collective intelligence, by supporting, via cloud communiting, virtuous behaviour from the bottom and raising the profile of a new way to understand urbanism displaying its individual and collecting benefits. Smart communities are increasingly characterise by platforms for service whose value lies in the offered facilities considered useful by the users, which in turn translate them into additional services to other users. A sort of mutual complicity is therefore important between the platform and the value-adding users, which can be implemented provided the platform/user relationship is "transparent", "open" and "authentic" hence included in the new citizenship pact.
Open Data and Big Data management is not limited to the administrative sphere or to decision-making processes, but requires the traditional urban planning’s cognitive model to be revised. It requires us not only to modify the protocols on which we base the plan's knowledge, but also to create new planning instruments. Hence, the first forms of Open-source Urbanism (Sassen, 2011). We should therefore begin to outline it and experience its practices in order to identify the main application protocols. We find ourselves in a smarter dynamic and innovative context therefore. Above all, it is shared and open, and ought to be also more “senseable”, aware and responsible. A proper Cloud Governance, not to be turned into a new mantra however: it ought to cooperate with leaderships and technocracies, with the directors and planners of the change, the actors in the transformation and the civil society to understand the extent to which the issue of openness and transparency involve their organizations, be it businesses, institutions, communities or universities. And there is more: the effort needed to follow this path, which leaves no room for alibis or laziness.
Planning in the information cloud age requires new maps, new sensors to detect obstacles, new tools for tracking the direction, but especially new eyes to not lose sight of the horizon.
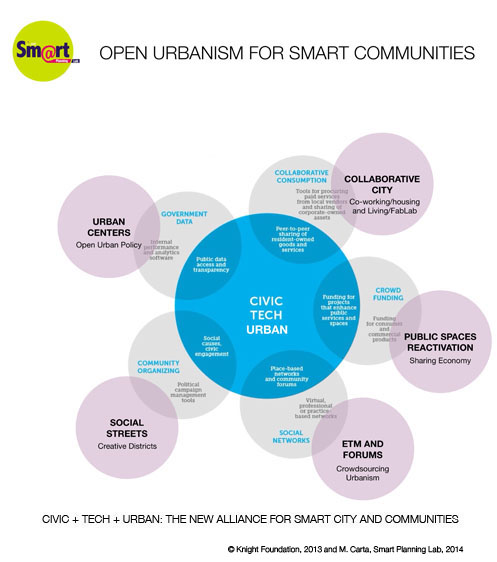
#SMART PLANNING PROTOCOL
ICT advantages within planning and management processes are especially clear today, as maps, data and assessment models are increasingly becoming a common heritage: the integration of web and wiki technologies with GIS applications is a very fruitful way to improve the chances of constructive interaction between citizens, policy makers and the wise skills at stake within the urban planning processes. On cloud technologies, popular among professional and consumers alike, allow regular updates directly from the source through a steady integration of decentralized databases. Georeferenced systems are central to decision-making processes at local and regional level, facilitating decisions of institutional and entrepreneurial actors, for example by sharing land knowledge, encouraging fast-tracking of administrative procedures. Shared databases can encourage public-private partnerships and project financing by making data, information and feasibility studies available to technical offices or by ensuring multi-utilities contributions. Finally, the involvement of local partners or the international opening through an increasingly shared regulatory and planning power can thus be enhanced.
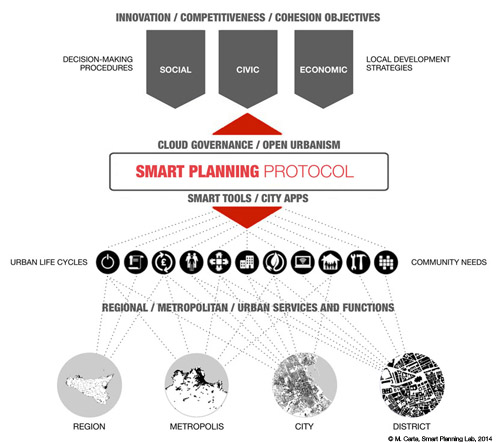
The experimentation, carried out in several local realities, of GIS network projects, aimed at promoting networking of cities, is included within the broader challenge of promoting cloud governance as a new dimension of local development. Community is the sphere of ICT integration into urban policies where the communicative potential is best expressed, and added value is ensured, namely the combination of actors who, out of a common interest, interact within networks by carrying out transactions and exchanges, reporting problems and sharing solutions, developing projects and promoting actions aimed at increasing the added value. Land management as a system of interconnected sensors, together with interfaces and City Apps, for example, can encourage the setting up of virtual districts (in the fields of production, tourism, food, culture) based on cloud computing dedicated to SMEs with the goal of restoring the local system's competitive advantages, stimulating the region's integrated development by linking businesses with other global enterprises networks. The local districts philosophy will lead city networks to compete in the global market as local network systems, employing three important competitive resources: geolocalised information, digital connections and citizen networks.
The spreading of sensors, electronic networks and urban life apps has created a proper urban cyber-physical space, consisting of the constant interaction between physical components and digital networks, tangible actions and intangible feedback. "We are at the onset of a hybrid dimension between the digital and material world, where the Internet is invading the physical space" – claims Carlo Ratti – by identifying it, making it attractive and setting it up for social uses, which are expected to gather the citizens in smart places connected to the network and providing services.
[extracted from M. Carta, Reimagining Urbanism. Creative, Smart and Green Cities for the Changing Times, Trento-Barcelona, ListLab, 2014]
|
#PROJECT PARTNERS
The i-NEXT Project is based on energy efficiency of buildings and the theme of sustainable mobility and logistics, powered by energy from renewable sources. The interweaving of the two themes can make available the public administration management some integrated technology solutions able to contain the economic, environmental and social effects from energy consumption and mobility of people and goods.
The Scientific Coordinator is Laura Andaloro (CNR-ITAE) and the Administrative Coordinator is Antonio Perniciaro (ITALTEL).
Presentation of the i-NEXT Project by the Scientific Responsible, Laura Andaloro

|
|
|
#ACTIVITIES
Coming soon
|
#LINKS |
 |
Reimagining Urbanism
Reimagining urbanism requires a rigorous exercise of will, responsibilities and competencies that are based on a system of urban governance based on new development pentagram: vision, strategy, design, rules and community. A different thought and an innovative chain of actions for the new times, able to reimagine the urban project. Cities of the future - smart, creative and green - must act within a state of perturbation that will not disappear soon. They will reactivate their capital guided by a planning can ensure the convergence of new forms of cultural, economic, environmental and social sustainability through the adoption of new visions of the future, either through the use of new paradigms but also through the quality of decisions and the performances of projects. [open] |
|
 |
Urban Makers: i nuovi cittadini bricoleurs
Makers, fablabers, urban farmers, startuppers, smart citizens and co-workers are the new protagonists of the contemporary city, acting in the urban, political and social stage of the third industrial revolution, which we have just entered. Citizens become producers, farmers enlivening dismissed and vacant areas of the city through urban agriculture, knowledge workers through workshops or creative incubators, cultural events organizers through crowfunding, managing theatres and cultural services. They are the new craftsmen of the digital revolution, thanks to their skills in turning with 3D printers, or in fixing objects at a time when recycling becomes more important than scrapping. These citizens-makers raise awareness of the new landscape, environment and energy saving sensitivity, renewing the traditional role of associations, no longer confined to pointing out the problem, but rather forming part of the solution, bearing its burden in an active and accountable way. [open] |
|
 |
Creative City: dynamics, innovations, actions
An up-to-date issue: the city investing in research, innovation and regeneration through culture and creativity are the vanguard in Europe. Cities with high quality of life, where culture, art, architecture and urban design have a powerful role and an active meaning. They are able to act on the social and urban dimension, on the generation of a new and evolving concept of urban culture. Creative City is a research-review, an atlas of urban, landscape and architectural projects, which collect some creative good practices for transforming the contemporary city, including Amsterdam, Barcelona, Bilbao, Bordeaux, Genoa, Hamburg, Lyon, Lisbon, Marseille, Newcastle, Palermo, Rotterdam and Valencia: city creating new urban culture. The "small creative capitals" are interpreted through an atlas of maps, data, informations and benchmarks useful to understand what happens and how it evolves the Europe of cities in which we live and which visions will be open up in next years. [open] |
|
 |
Protocollo REDS. Ripensare la città ecologica
The impact of the new ecological, technological and creative paradigms does not only affect our social actions in connection with the environment, but deeply impacts on the frames of mind, on methods and instruments of branches of learning which supply the principles and instruments to govern and shape the environment in which we live: territorial planning, town planning and urban project. The REDS Protocol ask for looking again at our territory as a generative resource, not only as consumption space, drawing of the energy of the new participatory mass where the talent of the young, the knowledge workers and the economies of sustainability mix and burst out, thus producing a new territory that we have to learn how to explore, interpret, regulate and plan, shifting from the rhetoric of social cohesion to the need of facing the new forms of conflicts which in the city find their genesis and outbreak. [open] |
|
|
|